Eur J Dermatol. 2000 Jun;10(4):265-8.
Source
Department of Dermatology, Philipp University, Deutschhausstrasse 9, D-35033 Marburg, Germany.
Abstract
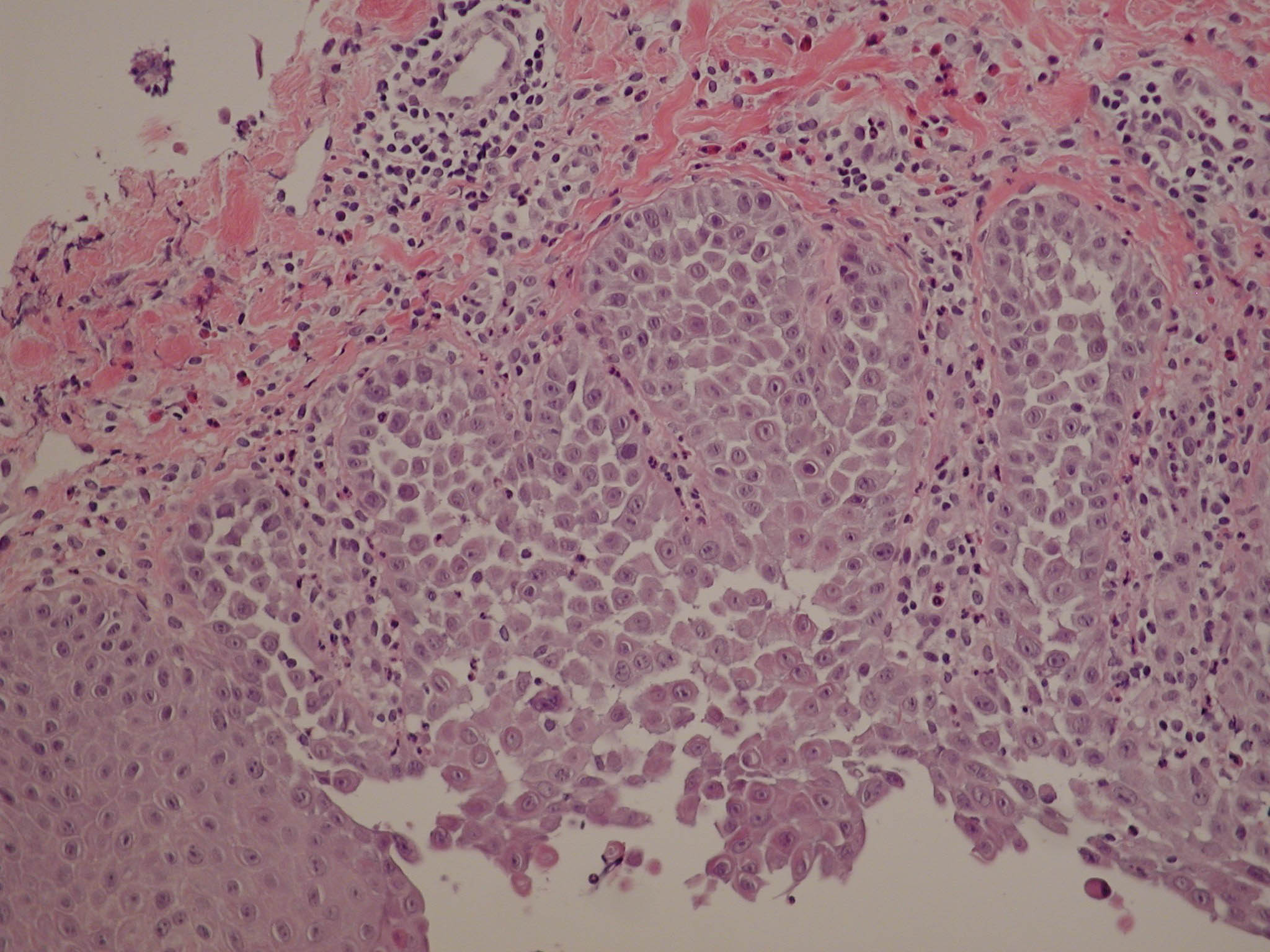
In autosomal dominant skin conditions, two different types of segmental manifestation can be distinguished. Type 1 represents heterozygosity for a postzygotic mutation, resulting in a degree of severity similar to that of the nonmosaic phenotype. Type 2 reflects loss of heterozygosity and shows an excessively pronounced involvement superimposed on the ordinary nonsegmental phenotype. We describe the clinical, histopathological and therapeutic aspects of the first case of type 2 segmental manifestation of Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD). A 24-year-old woman with a family history of HHD comprising four generations, presented with lesions of erythema and blistering arranged in a unilateral pattern following the lines of Blaschko. The disorder was first noted at the age of 3 months. At the age of 24 years, additional scattered symmetrical lesions involving the axillary and inguinal folds were noted. Histopathological examination of the severely involved linear skin areas revealed pronounced acantholysis within the deep adnexal structures, whereas clinically unaffected skin showed the typical histopathological features of the heterozygous phenotype with suprabasal clefting and acantholysis sparing the adnexae. Dermabrasion was performed in the areas of segmental involvement. During a follow-up period of one year, no recurrence was noted, but 18 months after dermabrasion a recurrence was present in the left submammary and left perianal regions. This therapeutic resistance to dermabrasion may be explained by the presence of acantholysis within the adnexal structures of the skin as found in type 2 segmental HHD.